बारिश को कैसे नापा जाता है?
सबसे पहले जानते हैं वर्षा की वैज्ञानिक परिभाषा क्या है?
वर्षण या अवक्षेपण एक मौसम विज्ञान की प्रचलित शब्दावली है जो वायुमण्डलीय जल के संघनित होकर किसी भी रूप में पृथ्वी की सतह पर वापस आने को कहते हैं। वर्षण के कई रूप हो सकते हैं जैसे वर्षा, फुहार, हिमवर्षा, हिमपात और ओलावृष्टि इत्यादि। अतः वर्षा वर्षण का एक रूप या प्रकार है।
वर्षा का मापन
असल में वर्षा का मापन और कुछ नहीं सिंपल सा तरीका हैं जिसमें एक फ्लास्क या पात्र जिसका अनुप्रस्थ काट ऊपर से नीचे तक एक समान होता हैं और खुला मुंह भी अनुप्रस्थ काट के बराबर होता हैं। इसे बारिश में सीधा खड़ा रखने पर बारिश के बाद पात्र में भरे पानी की मात्रा की ऊंचाई कुल वर्षा की माप को बताती हैं अर्थात इसे हम यह समझ सकते हैं की एक खुला टैंक जो पैंदे से खुली सतह तक एक समान हैं, मे वर्षा के बाद जितने मिलीमीटर या इंच पानी भर जाता हैं वर्षा की नाप को दर्शाता हैं।

आइए और सिंपल तरीके से समझते हैं आपकी छत अगर एकदम प्लेन है थोड़ा सा भी ढलान नहीं हैं और दीवारें भी एकदम खड़ी हैं तो पानी निकासी के पाइप को पूरी तरह से बंद करके बरसात के बाद सिंपल से स्केल से नापने पर जो रीडिंग मिलीमीटर सेंटीमीटर या इंच में मिलती हैं वही वर्षा की कुल मात्रा है।
वर्षा मापी यंत्र कोई विशेष वैज्ञानिक उपकरण नहीं हैं यह सिंपल सा बेलनाकार फ्लास्क होता हैं जिस पर मिलीमीटर या सेंटीमीटर में रीडिंग या पैमाना अंकित होता हैं इस फ्लास्क की मोटाई अंदर से ऊपर से नीचे तक एक समान होती है या जिसके ऊपर एक कीप रखा जाता हैं जिसके खुले मुंह का क्षेत्रफल ज्ञात होता हैं और फ्लास्क जो बेलनाकार होता हैं उसके अनुप्रस्थ काट का क्षेत्रफल भी ज्ञात होता हैं, को वर्षा के दौरान खुली जगह पर रखने पर फ्लास्क में जितना पानी भरता हैं उस रीडिंग से, फ्लास्क के अंदर के अनुप्रस्थ काट से कीप के खुले मुंह के क्षेत्रफल के अनुपात का गुणा करने पर कुल वर्षा की मात्र प्राप्त होती है।
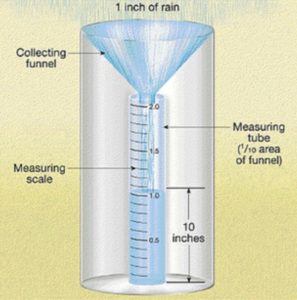
आइए इस गणित को विस्तार से उदाहरण के साथ समझते हैं मान लीजिए फ्लास्क या पात्र के अनुप्रस्थ काट का क्षेत्रफल 2 वर्ग सेंटीमीटर हैं और फ्लास्क के ऊपर रखे कीप के खुले मुंह का क्षेत्रफल 5 वर्ग सेंटीमीटर हैं और फ्लास्क में अगर 15 मिलीमीटर ऊंचाई तक पानी इकट्ठा हुआ तो 15x 2/5= 6 मिलीमीटर कुल वर्षा हुई।
सुविधा के लिए आधुनिक वर्षा मापी में रीडिंग फ्लास्क के अनुप्रस्थ काट तथा कीप के खुले मुंह के अनुप्रस्थ काट के अनुपात में ही लिखी जाती है, जिससे सीधे-सीधे रीडिंग देखकर बिना गणना के वर्षा के माप का पता चलता है।
आप कीप और फ्लास्क या पात्र के खुले मुंह का क्षेत्रफल निम्न सूत्र से निकाल सकते हैं क्योंकि कीप और फ्लास्क का खुला मुंह एक वृत्त के रूप में होता है।
किसी वृत्त का क्षेत्रफल निकालने का फ़ॉर्मूला हैः क्षेत्रफल = पाई (π) x त्रिज्या (r) का वर्ग. यानी, A = πr2. यहां, पाई का मान लगभग 3.14 या 22/7 होता है।
वर्षा को मापने वाले यंत्र को वर्षामापी कहते हैं। इसे कई नामों से जाना जाता है, जैसे कि प्लूवियोमीटर, ओम्ब्रोमीटर, हाइटोमीटर, और यूडोमीटर।
वर्षा मापन के दौरान रखी जाने वाली सावधानियां-
वर्षा मापी को जमीन थोड़ा लगभग आधा मीटर ऊपर स्थापित किया जाता है जिससे कि पृथ्वी की या किसी अन्य सतह से टकराकर पानी की बूंदे वर्षा मापी में नहीं गिरे और वर्षा के मापन को प्रभावित नहीं करें।
वर्षा मापी को एकदम खुले स्थान या खुली छत पर स्थापित करें जिससे कि वर्षा के दौरान हवा से आसपास के अवरोधों से वर्षा का मापन प्रभावित नहीं।
बरसात का मापन मौसम विज्ञान और जल संसाधन विभाग द्वारा सभी क्षेत्रों में विभिन्न वर्षा माफी इकाइयों से करते हैं।
आइए जानते हैं भारत मे वर्षा से संबंधित कुछ तथ्यों के बारे में-
भारत में सबसे ज़्यादा बारिश मेघालय के माउसिनराम में होती है। मासिनराम में सालाना औसतन 11,872 मिलीमीटर (467.4 इंच) बारिश होती और इसे पृथ्वी पर सबसे नम जगह माना जाता है। गिनीज़ बुक ऑफ़ वर्ल्ड रिकॉर्ड्स में भी मासिनराम का नाम सबसे ज़्यादा नम जगह के तौर पर दर्ज है।
भारत में सबसे कम बारिश राजस्थान के जैसलमेर में होती है। जैसलमेर का औसत 165 एमएम बारिश होती है।
भारत में होने वाली बारिश का बंटवारा इस प्रकार है-
| क्र. स. | मानसून | समय | प्रतिशतता |
| 1 | दक्षिण-पश्चिम मानसून | जून से सितंबर | 75% |
| 2 | उत्तर-पूर्वी मानसून | अक्टूबर से दिसंबर | 13% |
| 3 | पूर्व मानसून चक्रवात | अप्रैल और मई | 10% |
| 4 | पश्चिमी विक्षोभ | दिसंबर से फ़रवरी | 2% |
Read in English
How is rain measured?
During rainy days, we often get to see in the news that so many millimeters or so many inches of rain fell at this place, then a question definitely arises in the mind that how is rain measured? And can we measure rain at home too? First of all, the answer to this question is yes, we can easily measure rainfall in inches, centimeters or millimeters at home too.
So let us know about the method of measuring rainfall and the unit of measurement of rainfall.
First of all, let us know what is the scientific definition of rain?
Precipitation is a popular terminology of meteorology which refers to the condensation of atmospheric water and its return to the earth’s surface in any form. There can be many forms of precipitation such as rain, drizzle, snowfall, snow and hailstorm etc. Therefore, rain is a form or type of precipitation.
Measurement of Rainfall
Actually, the measurement of rainfall is nothing but a simple method in which a flask or container whose cross section is uniform from top to bottom and the open mouth is also equal to the cross section. If it is kept upright in the rain, the height of the amount of water filled in the container after the rain tells the measurement of total rainfall, that is, we can understand it that an open tank is uniform from the bottom to the open surface, the number of millimeters or inches of water that fills it after the rain shows the measurement of rainfall.
Let us understand in a more simple way, if your roof is completely flat, there is not even a slight slope and the walls are also completely straight, then after closing the water drainage pipe completely, the reading obtained in millimeters, centimeters or inches on measuring with a simple scale after the rain is the total amount of rainfall.
Rain gauge is not a special scientific instrument. It is a simple cylindrical flask on which the reading or scale is marked in millimeters or centimeters. The thickness of this flask is the same from top to bottom, or a funnel is placed on the flask, the area of the open mouth of which is known and the area of the cross section of the flask which is cylindrical is also known. When the flask is kept in an open place during rain, the amount of water that fills in it, by multiplying that reading with the ratio of the area of the open mouth of the funnel to the cross section inside the flask, the amount of total rainfall is obtained.
Let us understand this mathematics in detail with an example, suppose the area of the cross section of the flask or container is 2 square centimeters and the area of the open mouth of the funnel placed above the flask is 5 square centimeters and if water collects up to a height of 15 millimeters in the flask, then 15 x 2/5 = 6 millimeters of total rainfall occurred.
For convenience, the reading in modern rain gauges is written in the ratio of the cross section of the flask and the cross section of the open mouth of the funnel, so that the measurement of rainfall can be known without calculation by looking at the reading directly.
You can find the area of the open mouth of the funnel and the flask or the vessel by the following formula because the open mouth of the funnel and the flask is in the form of a circle.
The formula for finding the area of a circle is: Area = Pi (π) x square of radius (r). That is, A = πr2. Here, the value of Pi is approximately 3.14 or 22/7.
The instrument used to measure rainfall is called a rain gauge. It is known by many names, such as pluviometer, ombrometer, hyetometer, and eudiometer.
Precautions to be taken during rainfall measurement-
The rain gauge is installed a little about half a meter above the ground so that the water droplets do not fall into the rain gauge after hitting the earth or any other surface and do not affect the measurement of rainfall.
Install the rain gauge in a completely open place or on an open roof so that the measurement of rainfall is not affected by the surrounding obstructions from the wind during rainfall.
The measurement of rainfall is done by the Meteorological and Water Resources Department in all the regions with various rain gauge units.
Let us know about some facts related to rainfall in India-
The highest rainfall in India occurs in Mawsynram in Meghalaya. Mawsynram receives an average of 11,872 mm (467.4 inches) of rainfall annually and is considered the wettest place on earth. Mawsynram is also recorded as the wettest place in the Guinness Book of World Records.
The least rainfall in India occurs in Jaisalmer in Rajasthan. The average of Jaisalmer is 165 mm.
The distribution of rainfall in India is as follows-
| S. No. | Monsoon | Time | Percentage |
| 1 | South-west monsoon | June to September | 75% |
| 2 | North-east monsoon | October to December | 13% |
| 3 | Pre-monsoon cyclone | April and May | 10% |
| 4 | Western disturbance | December to February | 2% |
Leave a reply to कृत्रिम वर्षा कैसे होती है? – Dhakad blogs Cancel reply